Website atau aplikasi dengan traffic tinggi memerlukan arsitektur yang scalable, cepat, dan tahan banting. Kombinasi MySQL sebagai database dan Nginx sebagai web server/reverse proxy sering digunakan karena performa tinggi dan hemat resource.
Artikel ini membahas arsitektur high traffic, optimasi Nginx, MySQL tuning, caching, load balancing, dan best practices untuk production.
Contents
- 1 1. Prinsip Arsitektur High Traffic
- 2 2. Arsitektur Umum
- 3 3. Optimasi Nginx untuk High Traffic
- 4 4. Optimasi MySQL untuk High Traffic
- 5 5. Caching & Queue Layer
- 6 6. Scaling & High Availability
- 7 7. Security Layer
- 8 8. Monitoring
- 9 9. Studi Kasus High Traffic
- 10 10. Best Practices
- 11 Kesimpulan
- 12 Related Posts
1. Prinsip Arsitektur High Traffic
- Separation of Concerns
- Pisahkan web server (Nginx) dan database server (MySQL)
- Backend application (Node.js / PHP) di layer tersendiri
- Horizontal Scaling
- Tambah server web / backend sesuai traffic → lebih hemat daripada vertical scaling
- Caching Layer
- Gunakan Nginx cache, Redis / Memcached, MySQL query cache
- Load Balancing
- Nginx dapat membagi request ke beberapa backend application → mencegah bottleneck
- High Availability
- MySQL Master-Slave atau Cluster → failover jika master down
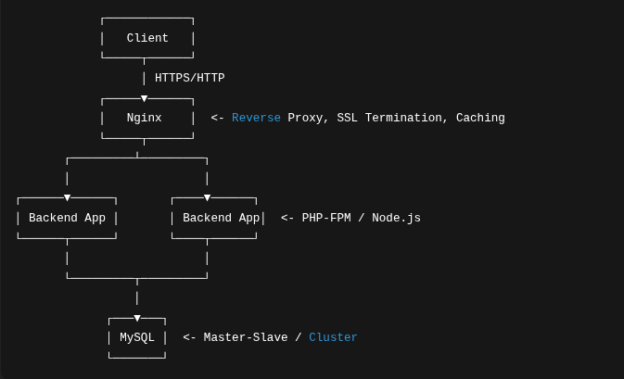
2. Arsitektur Umum
┌────────────┐
│ Client │
└─────┬──────┘
│ HTTPS/HTTP
┌─────▼──────┐
│ Nginx │ <- Reverse Proxy, SSL Termination, Caching
└─────┬──────┘
┌─────────┴─────────┐
│ │
┌──────▼──────┐ ┌────▼──────┐
│ Backend App │ │ Backend App│ <- PHP-FPM / Node.js
└──────┬──────┘ └────┬──────┘
│ │
└─────────┬─────────┘
│
┌───▼───┐
│ MySQL │ <- Master-Slave / Cluster
└───────┘
- Nginx menangani request & caching → backend fokus ke business logic
- Backend menulis ke MySQL Master, membaca dari Slave
- Query berat dapat dialihkan ke cache (Redis / Memcached)
3. Optimasi Nginx untuk High Traffic
3.1 Worker & Connections
worker_processes auto;
worker_connections 10240;
keepalive_timeout 65;
- Sesuaikan dengan CPU & jumlah concurrent connections
3.2 Caching
- Static content:
location ~* \.(jpg|jpeg|png|gif|ico|css|js)$ {
expires 30d;
add_header Cache-Control "public, no-transform";
}
- Dynamic microcaching:
proxy_cache_path /var/cache/nginx levels=1:2 keys_zone=mycache:10m max_size=1g inactive=60m use_temp_path=off;
server {
location / {
proxy_pass http://backend;
proxy_cache mycache;
proxy_cache_valid 200 5s;
proxy_cache_use_stale error timeout updating;
}
}
3.3 Load Balancing
upstream backend {
least_conn;
server backend1.example.com;
server backend2.example.com;
}
server {
location / {
proxy_pass http://backend;
}
}
- Metode least_conn ideal untuk backend dengan performa berbeda
- Nginx bisa handle SSL termination dan rate limiting
4. Optimasi MySQL untuk High Traffic
4.1 Konfigurasi MySQL
- Buffer & cache tuning:
[mysqld]
innodb_buffer_pool_size = 2G # 50-70% RAM server
innodb_log_file_size = 512M
query_cache_size = 64M
max_connections = 500
- InnoDB → performa transaksi tinggi, row-level locking
4.2 Master-Slave Replication
- Master → handle write
- Slave(s) → handle read query
- Meningkatkan read scalability & failover
4.3 Indexing & Query Optimization
- Gunakan index untuk kolom yang sering dicari
- Hindari
SELECT *→ spesifik kolom - Gunakan EXPLAIN untuk menganalisis query
4.4 Connection Pooling
- Gunakan pool (PHP-FPM, Node.js, ProxySQL) → mengurangi overhead membuka koneksi MySQL
- Contoh Node.js:
mysql2pool, max 50 connection
5. Caching & Queue Layer
- Gunakan Redis / Memcached:
- Session store
- Query cache
- API response cache
- Gunakan queue system (RabbitMQ / Kafka) untuk job berat → tidak blok request user
6. Scaling & High Availability
6.1 Web & Backend
- Horizontal scaling dengan Nginx load balancing
- Auto-scaling server cloud jika traffic spike
6.2 Database
- MySQL Master-Slave → read/write separation
- Optional: MySQL Cluster / Galera → multi-master HA
6.3 CDN
- Gunakan CDN untuk static assets → mengurangi load VPS dan latency global
7. Security Layer
- SSL termination di Nginx → backend cukup HTTP
- Rate limiting → mencegah abuse / brute-force
- DDoS mitigation → limit connection & request
- Firewall & fail2ban → blokir IP mencurigakan
8. Monitoring
| Komponen | Tools |
|---|---|
| Nginx | access.log, error.log, Nginx Amplify, Grafana |
| Backend | PM2 (Node.js), PHP-FPM status, New Relic |
| MySQL | slow query log, performance_schema, Percona Monitoring |
| System | htop, iostat, netstat, Prometheus + Grafana |
- Pantau latency, CPU, RAM, connections, cache hit ratio
- Alert jika backend atau DB overload
9. Studi Kasus High Traffic
Startup e-commerce:
- Traffic: 50k concurrent user / hari
- Arsitektur:
- Nginx reverse proxy + caching
- Backend Node.js + PHP-FPM
- MySQL Master-Slave
- Redis untuk session & cache
- CDN untuk gambar
- Hasil:
- Response time <200ms
- Backend tetap ringan → hemat VPS cost
- Scalable dengan tambah backend server
10. Best Practices
- Pisahkan web server, backend, database
- Gunakan Nginx caching & load balancing
- Optimasi MySQL buffer & query
- Gunakan Redis/Memcached → kurangi query berat ke MySQL
- Load balancing read query ke MySQL slave(s)
- Implementasi SSL & security layer di Nginx
- Monitoring real-time → deteksi bottleneck cepat
- Horizontal scaling → tambah server saat traffic spike
- Gunakan CDN untuk static content
Kesimpulan
Arsitektur web high traffic dengan MySQL & Nginx memungkinkan:
- Scalable & resilient → handle ribuan hingga ratusan ribu concurrent user
- Fast response → caching & query optimization
- High availability → MySQL master-slave, Nginx failover
- Cost efficient → Nginx hemat resource, CDN mengurangi bandwidth
Dengan strategi ini, website production bisa tahan traffic tinggi, cepat, dan aman, sambil tetap hemat biaya infrastruktur.